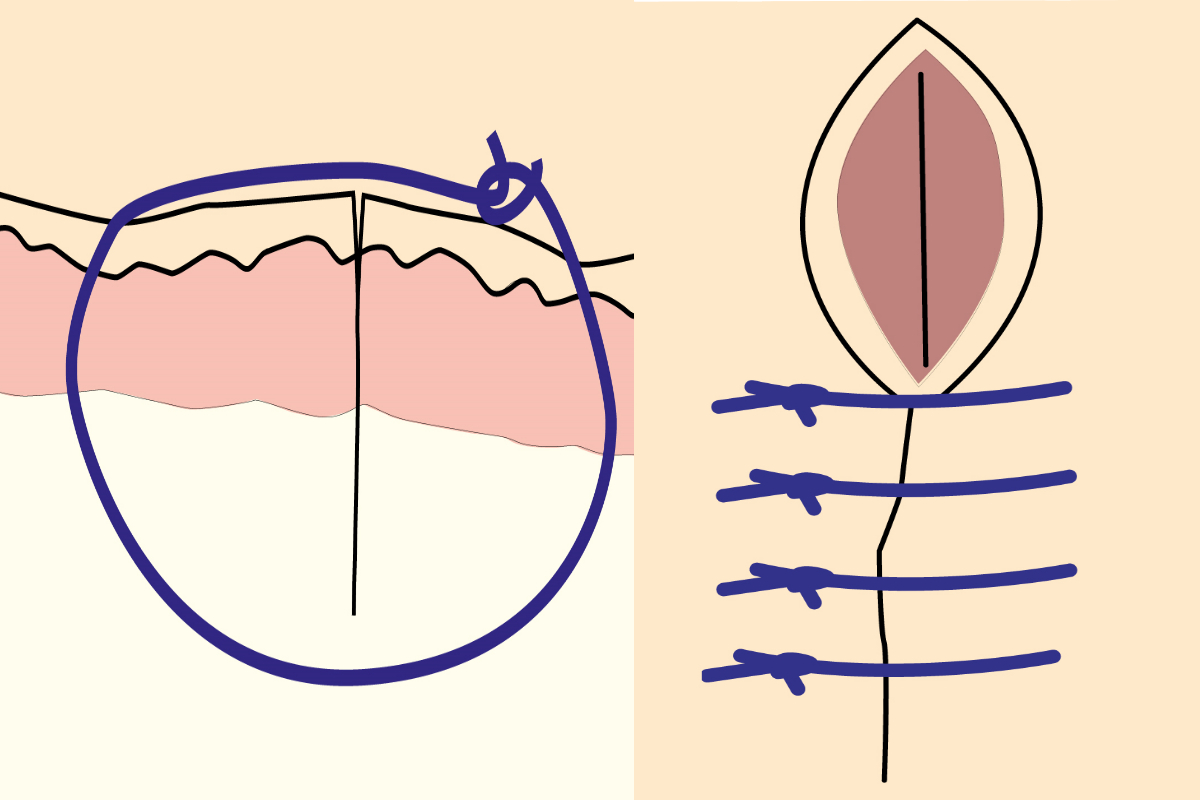
Inverting Suture Pattern
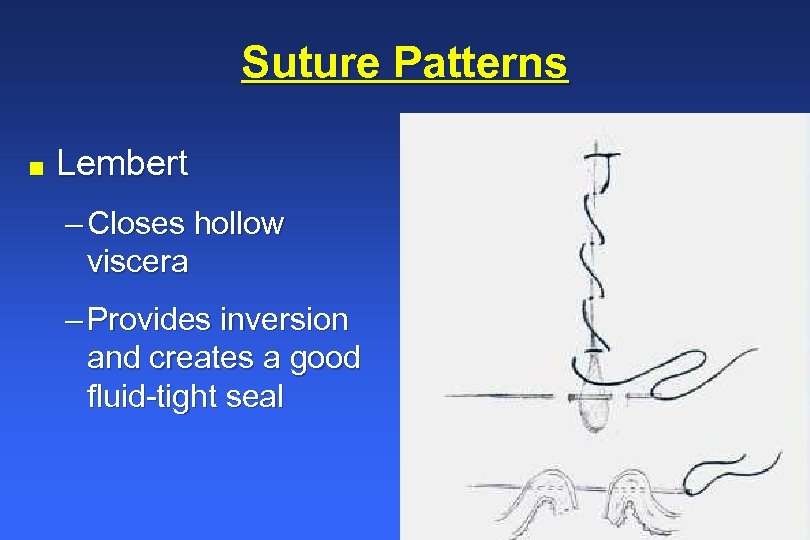
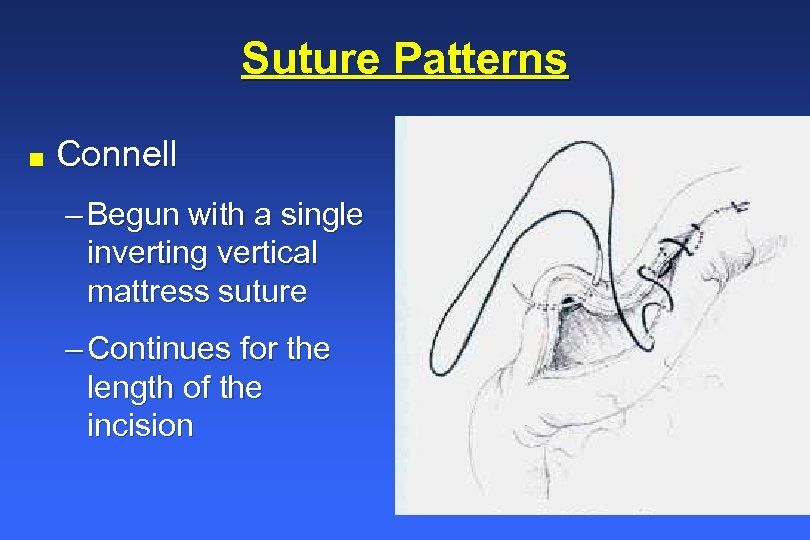
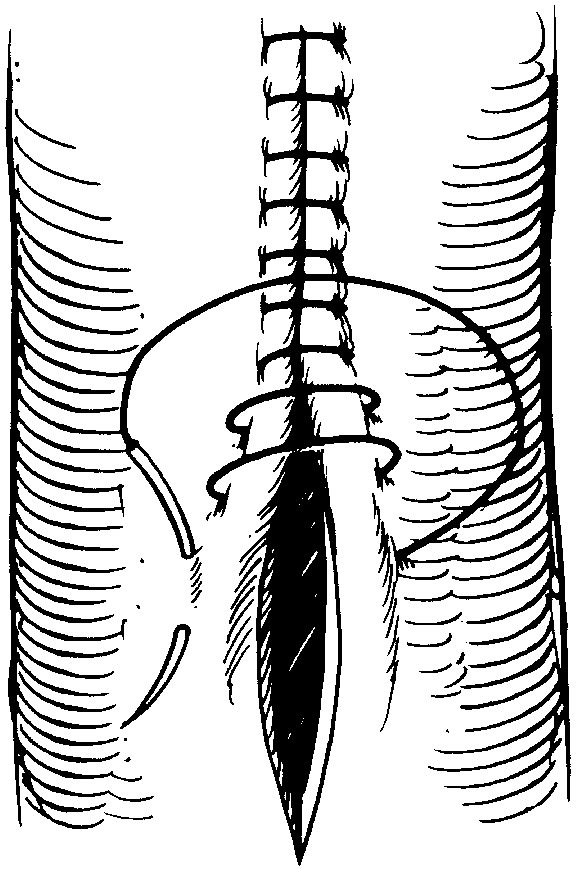
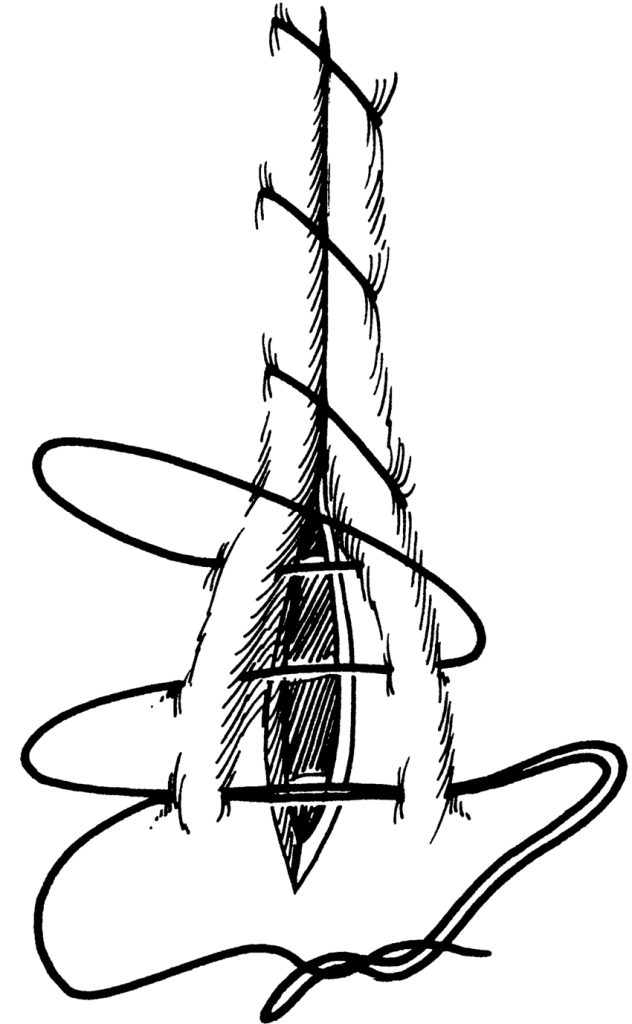
Inverting Suture Pattern - 45 most reptiles lack a diaphragm and have a single coelom, intracoelomic testes, a common cloaca, and so forth. Web one layer is often described in the literature but that suture line becomes loose as the uterus contracts, making a second advisable. To create a water tight seal, secure the rumen to the skin using a continuous cushing pattern of 2. Patients that have had a diaphragmatic incision will require diaphragmatic closure and removal of intrathoracic air by transdiaphragmatic thoracocentesis or the placement of a chest tube. It penetrates the submucosa but does not penetrate the organ’s lumen. Web learn how to perform an inverting lembert suture pattern, a technique for tissue apposition in veterinary surgery, with this video tutorial from michigan state university. Web using the correct suture pattern will help to restore anatomical alignment of tissues, obliterate dead space, minimize tissue trauma and preserve blood supply to the tissues. Absorbable #2 with a swedged on needle is advised. Web cushing suture pattern: Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. The latter is the most effective. If done correctly, this pattern should invert the tissues enough to cover the first layer leaving only the knots of the inverting pattern visible. As well as being able to perform the basic patterns, it important to be familiar with their basic properties so you will be able to decide when their use is appropriate. It runs parallel to the incision line by taking tissue bites on either side of the incision. A bite is taken symmetrically at an equal distance from either side of the wound and pulled tight. Two inverting suture lines (cushing or lembert) what layers to include? Inversion is usually desirable only to close hollow viscera to prevent leakage, but excessive inversion reduces luminal diameter. Web closing a gastrotomy in two layers. Web start the pexy by placing a suture (#2 pds or nylon) across the caudal aspect of the dorsal sheath. Web cushing suture pattern: Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web the suture patterns used in equine anastomoses can be classified according to whether they invert, appose or evert the incised. That’s useful, especially in hollow organs, to prevent any liquid that may be present inside the lumen from escaping through the incision. Invert the seromuscular layer with a cushing suture pattern, taking bites parallel to the incision line that do not penetrate the lumen. Web closing a gastrotomy in two layers. There is no need to include the abomasum in. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Invert the seromuscular layer with a cushing suture pattern, taking bites parallel to the incision line that do not penetrate the. Web closing a gastrotomy in two layers. Web this can be via use of a rumen board, rumen protector or by creating a water tight seal by use of an inverting suture pattern. Web the suture patterns used in equine anastomoses can be classified according to whether they invert, appose or evert the incised edges of the bowel and can. Web closing a gastrotomy in two layers. Web start the pexy by placing a suture (#2 pds or nylon) across the caudal aspect of the dorsal sheath. Inversion is usually desirable only to close hollow viscera to prevent leakage, but excessive inversion reduces luminal diameter. Web the suture patterns used in equine anastomoses can be classified according to whether they. Web closing a gastrotomy in two layers. These patterns prevent leakage and minimize the risk of adhesions due to exposed suture. Web the continuous cushing pattern is often used for closing incisions in hollow viscera such as the stomach, urinary bladder and uterus. Inversion is usually desirable only to close hollow viscera to prevent leakage, but excessive inversion reduces luminal. Web cushing suture pattern: Web using the correct suture pattern will help to restore anatomical alignment of tissues, obliterate dead space, minimize tissue trauma and preserve blood supply to the tissues. Any inverting pattern can be used (lembert, utrecht, cushing). Web common suture patterns: Inversion is usually desirable only to close hollow viscera to prevent leakage, but excessive inversion reduces. Web closing a gastrotomy in two layers. Web surgical techniques in reptiles can be challenging, due to the wide variety of unique anatomic and physiologic characteristics. Secure the bite with a knot. These patterns prevent leakage and minimize the risk of adhesions due to exposed suture. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area. Michael ross demonstrates the cushing suture pattern and explains the difference between the cushing and connell suture patterns. If done correctly, this pattern should invert the tissues enough to cover the first layer leaving only the knots of the inverting pattern visible. Web inverting patterns turn the cut edges inward and minimize exposed suture. Two inverting suture lines (cushing or. To create a water tight seal, secure the rumen to the skin using a continuous cushing pattern of 2. Invert the seromuscular layer with a cushing suture pattern, taking bites parallel to the incision line that do not penetrate the lumen. Two inverting suture lines (cushing or lembert) what layers to include? Web an inverting pattern can sometimes be quite. Web common suture patterns: It runs parallel to the incision line by taking tissue bites on either side of the incision. As well as being able to perform the basic patterns, it important to be familiar with their basic properties so you will be able to decide when their use is appropriate. Invert the seromuscular layer with a cushing suture pattern, taking bites parallel to the incision line that do not penetrate the lumen. Web the continuous cushing pattern is often used for closing incisions in hollow viscera such as the stomach, urinary bladder and uterus. Absorbable #2 with a swedged on needle is advised. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous. These are used to close lumens in large animal species (intestines, bladders, uteri). There is no need to include the abomasum in this bite. Close the dorsal sheath using a simple continuous pattern. Fast, continuous, easy inverting suture technique for intestinal incision bites are taken parallel to the incision but the suture doesn’t pass right through the wall. That’s useful, especially in hollow organs, to prevent any liquid that may be present inside the lumen from escaping through the incision. Web using the correct suture pattern will help to restore anatomical alignment of tissues, obliterate dead space, minimize tissue trauma and preserve blood supply to the tissues. Web an inverting pattern can sometimes be quite useful, for example to invaginate a section of stomach wall when managing a patient with gastric dilatation and volvulus whose gastric mucosal viability is questionable. Web cushing suture pattern: 45 most reptiles lack a diaphragm and have a single coelom, intracoelomic testes, a common cloaca, and so forth.INVERTED SUTURES,Inverted Stitching, Inverting Sutures YouTube
Wound Healing and Suture Knowledge ASR Certification Prep
Inverting Suture PatternConnell; Cassidy Gillum YouTube
Wound Healing and Suture Knowledge ASR Certification Prep
Suturing inverting suture patterns Large Animal Surgery
Cushing Suture Pattern Fast, Continuous, Easy Inverting Suture
Suturing inverting suture patterns Large Animal Surgery
Figure 1 from The inverting horizontal mattress suture applications in
Common Suture Patterns and Suture Techniques EndoGynecology
Common Suture Patterns and Suture Techniques EndoGynecology
Web The Use Of A Specific Suture Pattern May Vary Depending On The Area Being Sutured, The Length Of The Incision, The Tension At The Suture Line, And The Specific Need For Apposition, Inversion, Or Eversion Of The Tissues.
Suture Patterns Can Be Broadly Categorized As Interrupted Or Continuous.
Inversion Is Usually Desirable Only To Close Hollow Viscera To Prevent Leakage, But Excessive Inversion Reduces Luminal Diameter.
It Penetrates The Submucosa But Does Not Penetrate The Organ’s Lumen.
Related Post: