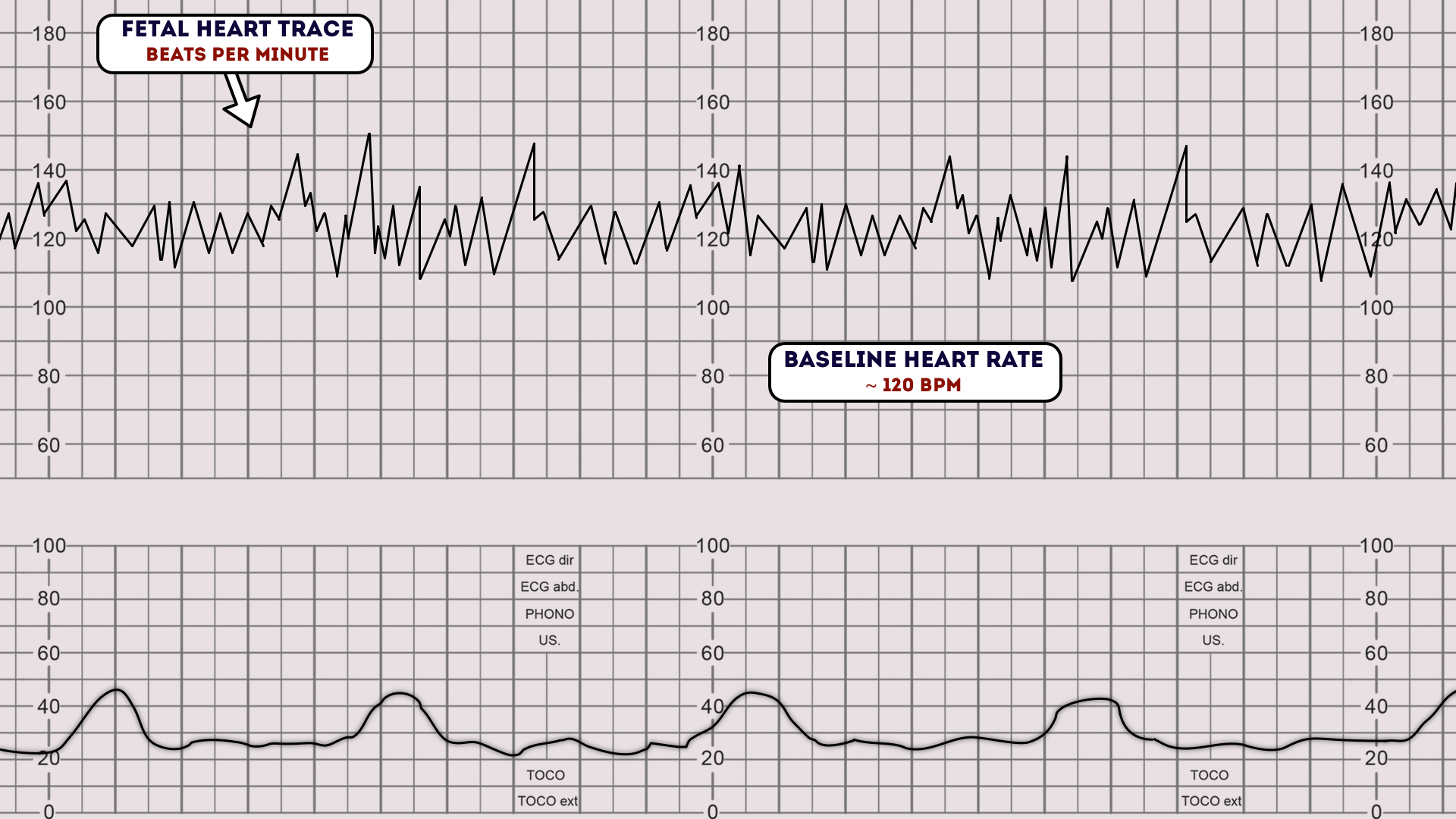
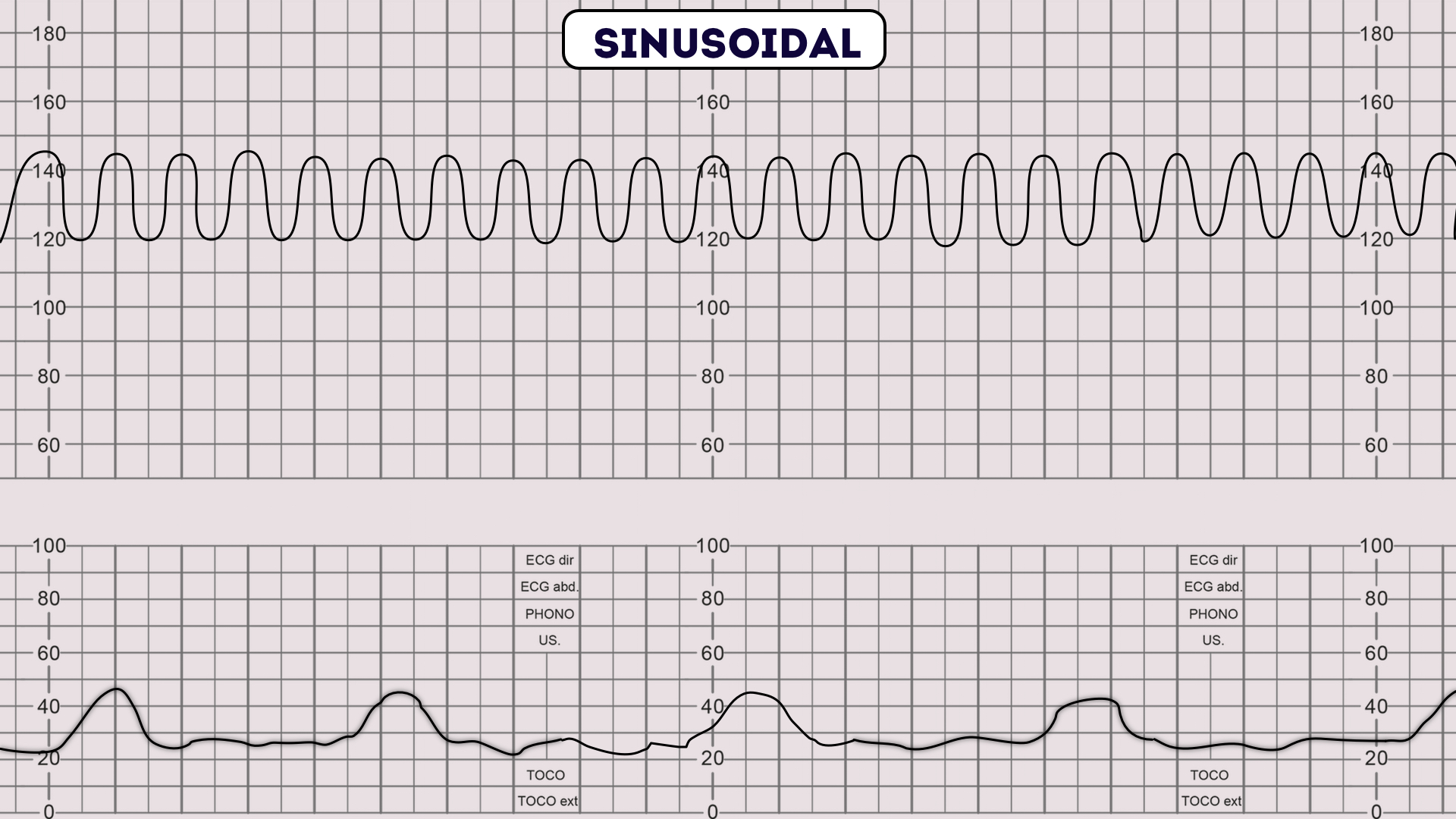
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns - Web your pregnancy care provider diagnoses fetal distress by reading the fetal heart rate. Web external fetal heart rate monitoring at 1 cm/min (top graph), 2 cm/min (middle graph), and 3 cm/min (bottom graph). The fetal heart rate may change as the fetus responds to conditions in the uterus. It is measurable sonographically from around 6 weeks and the normal range varies during gestation, increasing to around 170 bpm at 10 weeks and decreasing from then to around 130 bpm at term. Web changes or trends of fhr patterns over time. An abnormal fetal heart rate or pattern may indicate that the fetus is not getting enough oxygen or that there are other problems. Determine the presence of accelerations or decelerations from baseline. By monitoring your baby’s heart rate, your provider can tell if the heart rate is too high or low or changing too much. Fetal heart rate can provide lots of information about your baby’s health. Web your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor. Determine the presence of accelerations or decelerations from baseline. By understanding the physiologic and pathophysiologic basis of fhr monitoring, as well as its capabilities and limitations, the clinician can reduce the need for interventions. Very early in pregnancy, it is typically around 110 bpm. Web the main method is monitoring fetal heart rate patterns, usually in relation to uterine contractions. Fetal heart rate can provide lots of information about your baby’s health. The following tables are reproduced from cg190. A specific definition of shr was made in order to elucidate its clinical significance. Web nonreassuring fhr patterns are common and quite nonspecific. Frequency and intensity of uterine contraction. Web a normal fetal heart rate (fhr) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) in the in utero period. An abnormal fetal heart rate or pattern may indicate that the fetus is not getting enough oxygen or that there are other problems. Web the average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute, and can vary five to 25 beats per minute. The average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute. Web. Starting soon after a woman in labor is admitted to the hospital, the doctor or another health care professional monitors the fetus’s heartbeat either periodically or continuously. Eart rate monitoring (efm) is used in the vast majority of all labors in the united states. Web intrapartum assessment of the fetal heart rate, or fhr for short, refers to the assessment. This paper is only available as a pdf. Web they provide details of fetal heart rate classification systems used in studies included for the review question about interpretation of cardiotocograph traces. Web sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern: Web the average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute, and can vary five to 25 beats per minute.. Web sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern: Eart rate monitoring (efm) is used in the vast majority of all labors in the united states. Web external fetal heart rate monitoring at 1 cm/min (top graph), 2 cm/min (middle graph), and 3 cm/min (bottom graph). Identify changes or trends in fhr patterns over time Web goals of intrapartum fetal monitoring include rapid. It is measurable sonographically from around 6 weeks and the normal range varies during gestation, increasing to around 170 bpm at 10 weeks and decreasing from then to around 130 bpm at term. Checking the fetal heart rate is a good way to find out if. Web in monitoring the fetal status, clinicians should pay attention to the baseline fetal. Its definition and clinical significance. Checking the fetal heart rate is a good way to find out if. Web 3 steps for distinguishing heart rate patterns. Baseline fhr and variability are influenced by changes in cns activity, volume status, baroreceptor stimulation, and chemoreceptor stimulation. Web a normal fetal heart rate (fhr) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute. Web a normal fetal heart rate (fhr) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) in the in utero period. Web your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor. This is combined with ultrasonography in some assessment methods. Web to improve the timely detection of fetal hypoxia and/or acidemia during labor, we recently. Web your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor. Web intrapartum assessment of the fetal heart rate, or fhr for short, refers to the assessment of the fhr and rhythm in response to uterine activity during the intrapartum period, which refers to the time of pregnancy from the onset of labor to delivery of the. Web a normal heart rate for a fetus can range from 110 to 160 beats per minute (bpm). Baseline fhr and variability are influenced by changes in cns activity, volume status, baroreceptor stimulation, and chemoreceptor stimulation. The average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute. Fetal heart rate can provide lots of information about your baby’s. Web in this video, meris covers the normal and abnormal fetal heart rate patterns, including causes and nursing interventions to take for each. Web external fetal heart rate monitoring at 1 cm/min (top graph), 2 cm/min (middle graph), and 3 cm/min (bottom graph). Eart rate monitoring (efm) is used in the vast majority of all labors in the united states.. Web 3 steps for distinguishing heart rate patterns. It can vary by 5 to 25 beats per minute. Web your pregnancy care provider diagnoses fetal distress by reading the fetal heart rate. Web changes or trends of fhr patterns over time. Baseline fetal heart rate (fhr): The fetal heart rate may change as the fetus responds to conditions in the uterus. Web your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor. Baseline fhr and variability are influenced by changes in cns activity, volume status, baroreceptor stimulation, and chemoreceptor stimulation. Checking the fetal heart rate is a good way to find out if. By monitoring your baby’s heart rate, your provider can tell if the heart rate is too high or low or changing too much. Fetal heart rate (hr) monitoring can be manual and intermittent, using a fetoscope for auscultation of fetal hr. A review was made of the available literature on the sinusoidal heart rate (shr) pattern. Starting soon after a woman in labor is admitted to the hospital, the doctor or another health care professional monitors the fetus’s heartbeat either periodically or continuously. Web they provide details of fetal heart rate classification systems used in studies included for the review question about interpretation of cardiotocograph traces. Web a normal heart rate for a fetus can range from 110 to 160 beats per minute (bpm). Determine the presence of accelerations or decelerations from baseline.OB Fetal Heart Tone Monitoring DecelerationsLearn how to view, detect
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns
fetal heart rate monitor interpretation Newborn nursing, Nursing
Normal Fetal Heart Rate Chart
Fetal heart rate patterns
How to Read a CTG CTG Interpretation Geeky Medics
Fetal heart rate patterns
fetal monitor patterns showing normal, tachycardia, early deceleration
Sinusoidal fetal heart rate
Sawtooth fetal heart rate pattern due to in utero fetal central nervous
Very Early In Pregnancy, It Is Typically Around 110 Bpm.
At The End Of The Video, Meris Provides A Quiz To Help You Test Your Knowledge Of.
Web Nonreassuring Fhr Patterns Are Common And Quite Nonspecific.
This Is Combined With Ultrasonography In Some Assessment Methods.
Related Post: