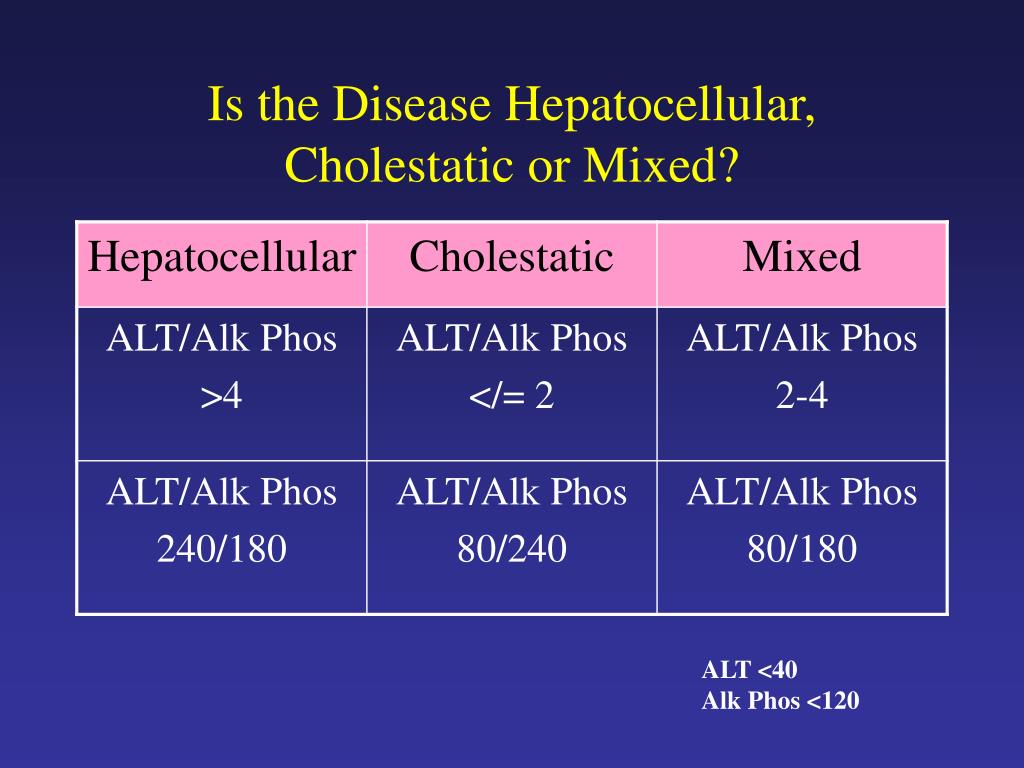
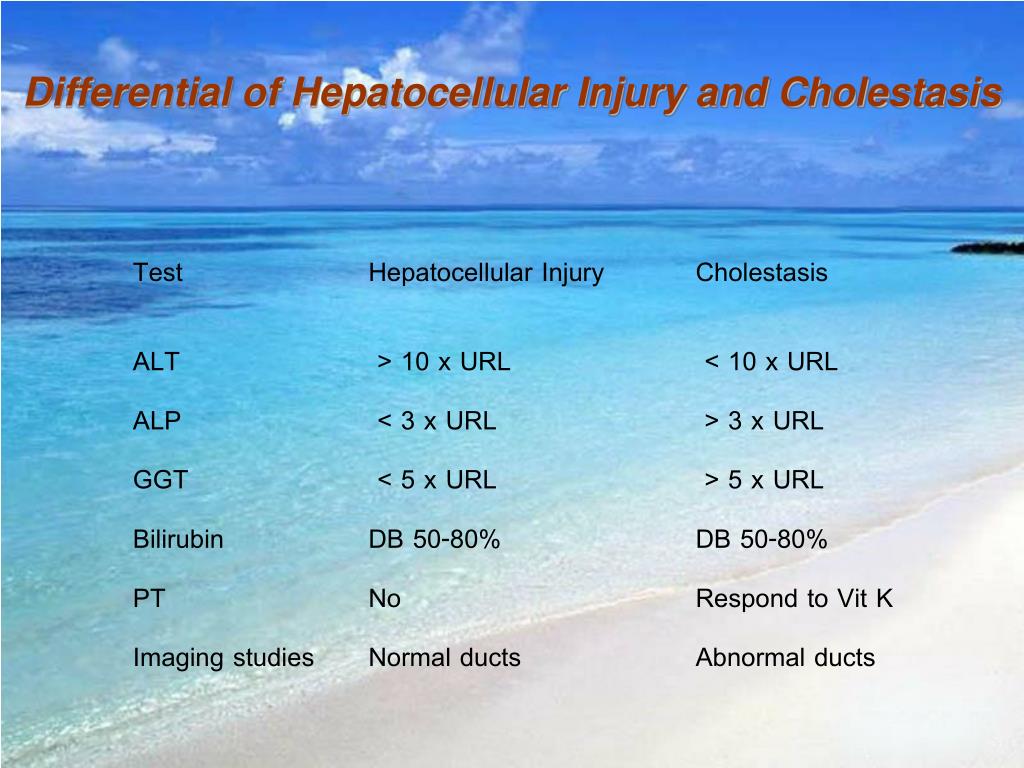
Cholestatic Vs Hepatocellular Pattern
Cholestatic Vs Hepatocellular Pattern - Web an r ratio of greater than 5 defines hepatocellular dili, whereas cholestatic dili is characterized by an r ratio of less than 2. Web there are four major types of liver injury: Web the cholestatic pattern of liver function test abnormalities indicates biliary obstruction. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. The pattern occurs when there is a disproportionate elevation in alkaline phosphatase (alp) compared to alanine aminotransferase (alt) and aspartate aminotransferase (ast). Web overall analysis of liver function tests (lft) transaminitis: Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Ratio of ast and alt can be useful in differential. Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia pattern, each of which can be acute, subacute, or chronic in presentation. Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia pattern, each of which can be acute, subacute, or chronic in presentation. Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. Ratio of ast and alt can be useful in differential. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Web the pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether the pathology is primarily cholestatic or hepatocellular: Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1). Dili is characterized as mixed if the r ratio is between 2 and 5. A hepatocellular pattern is marked by isolated or predominant elevations. The predominant laboratory abnormality defines the pattern of injury. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Web there are four major types of liver injury: Web using a schematic approach that classifies enzyme alterations as predominantly hepatocellular or predominantly cholestatic, we review abnormal enzymatic activity within the 2 subgroups, the most common causes of enzyme alteration and suggested initial investigations. Web overall analysis of liver function tests (lft) transaminitis: The aim of this study was to. Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. Dili is characterized as mixed if the r ratio is between 2 and 5. The predominant laboratory abnormality defines the pattern of injury. The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of serum alp values in patients with hepatocellular liver. Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1). Web the pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether the pathology is primarily cholestatic or hepatocellular: Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. The predominant laboratory abnormality defines the pattern of injury. The pattern occurs when there is a disproportionate elevation in alkaline phosphatase (alp) compared to alanine aminotransferase. Web there are four major types of liver injury: The predominant laboratory abnormality defines the pattern of injury. Web the pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether the pathology is primarily cholestatic or hepatocellular: Web using a schematic approach that classifies enzyme alterations as predominantly hepatocellular or predominantly cholestatic, we review abnormal enzymatic activity within the 2 subgroups,. Generally not associated with cholestasis. The pattern occurs when there is a disproportionate elevation in alkaline phosphatase (alp) compared to alanine aminotransferase (alt) and aspartate aminotransferase (ast). Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia pattern, each of which can be acute, subacute, or chronic in. Web the three abnormal patterns that can be detected in liver function tests include the hepatocellular pattern, cholestatic pattern, and isolated hyperbilirubinemia pattern, each of which can be acute, subacute, or chronic in presentation. Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1). Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult.. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Generally not associated with cholestasis. The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of serum alp values in patients with hepatocellular liver injury and alt or ast values in patients with cholestasis. Web the pattern of alt to. Web there are four major types of liver injury: Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. Web the pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether the pathology is primarily cholestatic or hepatocellular: The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of serum alp values in patients with hepatocellular liver injury and alt or. Web using a schematic approach that classifies enzyme alterations as predominantly hepatocellular or predominantly cholestatic, we review abnormal enzymatic activity within the 2 subgroups, the most common causes of enzyme alteration and suggested initial investigations. Generally not associated with cholestasis. Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. Web the pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether. Web there are four major types of liver injury: Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. Web overall analysis of liver function tests (lft) transaminitis: Web an r ratio of greater than 5 defines hepatocellular dili, whereas cholestatic dili is characterized by an r ratio of less than 2. Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. The aim of this study was to document the predicted ranges of serum alp values in patients with hepatocellular liver injury and alt or ast values in patients with cholestasis. Web when both sets of enzymes are elevated, distinguishing between the two patterns of liver disease can be difficult. Dili is characterized as mixed if the r ratio is between 2 and 5. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Web the cholestatic pattern of liver function test abnormalities indicates biliary obstruction. Aminotransferases (ast, alt) generally associated with hepatocellular damage. Web there are four major types of liver injury: Web the pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether the pathology is primarily cholestatic or hepatocellular: The pattern occurs when there is a disproportionate elevation in alkaline phosphatase (alp) compared to alanine aminotransferase (alt) and aspartate aminotransferase (ast). Alt is more specific for liver damage than ast. Web an r ratio of greater than 5 defines hepatocellular dili, whereas cholestatic dili is characterized by an r ratio of less than 2. Hepatocellular, autoimmune, cholestatic, and infiltrative (table 1). Ratio of ast and alt can be useful in differential. Generally not associated with cholestasis. Web overall analysis of liver function tests (lft) transaminitis:Liver Enzymes (hepatic vs cholestatic patterns) Sketchy Medicine
PPT Work up of the Asymptomatic Patient with Liver Enzyme
Liver Histology Clinics in Liver Disease
Pin on Infographics
PPT Abnormal LFTs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID139175
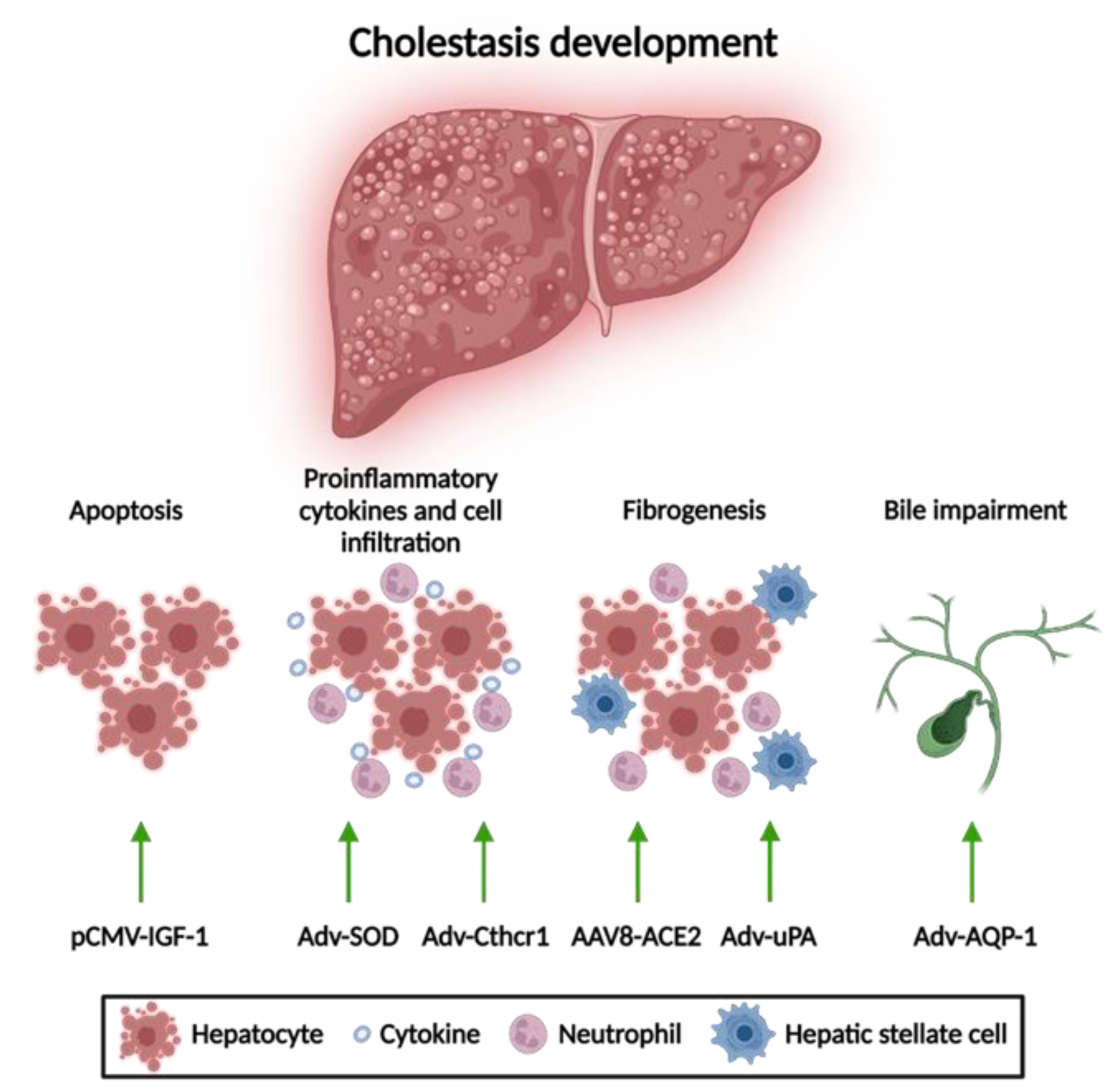
Gene Therapy for Cholestasis Encyclopedia MDPI
Liver function tests in primary care bpacnz
Laboratory Associations with Hepatocellular and Cholestatic Patterns of
PPT Liver Function Test s PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Liver Failure Case
The Predominant Laboratory Abnormality Defines The Pattern Of Injury.
Web Using A Schematic Approach That Classifies Enzyme Alterations As Predominantly Hepatocellular Or Predominantly Cholestatic, We Review Abnormal Enzymatic Activity Within The 2 Subgroups, The Most Common Causes Of Enzyme Alteration And Suggested Initial Investigations.
Web The Three Abnormal Patterns That Can Be Detected In Liver Function Tests Include The Hepatocellular Pattern, Cholestatic Pattern, And Isolated Hyperbilirubinemia Pattern, Each Of Which Can Be Acute, Subacute, Or Chronic In Presentation.
A Hepatocellular Pattern Is Marked By Isolated Or Predominant Elevations.
Related Post: